People who are bedridden or immobile are particularly concerned about bedsores, commonly referred to as pressure ulcers. They happen when long-term pressure damages tissue by lowering blood flow to the skin. In-home care, nursing homes, and hospitals, bedsores are a serious problem.
By shifting pressure, lowering friction, and improving comfort, positioning pads are essential in preventing bedsores. This article explores their role in maintaining skin integrity and improving care for at-risk patients.
What Are Bedsores?
Before discussing the role of positioning pads, it’s important to understand what bedsores are and why they occur.
When a person applies constant pressure to a certain area of their body, bedsores form. By limiting blood flow to the skin and deeper tissues, this pressure deprives them of nutrition and oxygen. As a result, the affected tissue starts to break down, leading to the formation of open wounds. Bedsores are most commonly found on bony prominences, where the skin is closest to the bone, such as the heels, sacrum, elbows, hips, and shoulders.
The stages of bedsores range from redness of the skin (Stage I) to open wounds that extend deep into the tissues, muscles, or bones (Stage IV). Bedsores can result in serious side effects such as infections, sepsis, and even death if treatment is not received.
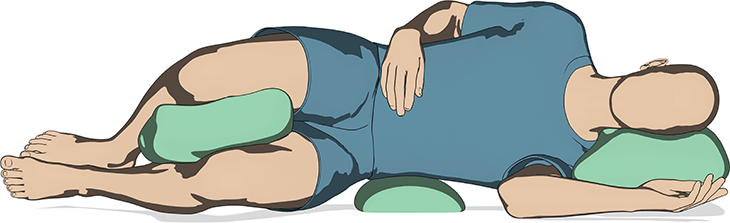
The Role of Positioning Pads in Preventing Bedsores
Positioning pads are devices designed to support the body in specific positions while redistributing pressure away from vulnerable areas. By using these pads, healthcare providers can prevent the prolonged pressure that leads to bedsores and improve the overall skin integrity of patients. Here’s how positioning pads contribute to pressure relief:
1. Redistribution of Pressure
One of the primary roles of positioning pads is to redistribute pressure away from areas at high risk of developing bedsores. When a patient lies in one position for an extended period, the weight of the body presses down on certain parts of the skin, causing pressure on the underlying tissue. Positioning pads help by creating a cushion between the body and the surface, such as a mattress or bed. This redistribution of pressure ensures that no single area bears the entire load, which is key to preventing tissue damage.
For example, in the supine position, where a patient lies on their back, the sacral area, heels, and elbows are at high risk of developing bedsores. Specialized heel protectors and sacral cushions reduce pressure on these areas by creating a buffer that redistributes the pressure to larger surface areas of the body. Heel and ankle pads provide cushioning for the heels and prevent the formation of pressure ulcers in this vulnerable region.
2. Cutting Down on Shear and Friction
Other important elements that have a role in the development of bedsores are friction and shear. The skin might become irritated and more prone to breakdown when it scrapes against objects like bedding, clothes, or other surfaces. Conversely, shear happens when the skin is dragged in one direction while the tissues underneath it move in another, usually when the skin is being repositioned.
Positioning pads made from materials such as foam, gel, or air can help reduce friction and shear by providing a smooth surface and preventing direct skin-to-surface contact. These pads, often used in conjunction with specialized mattresses, create a friction-free environment that minimizes the risk of skin abrasion. For example, an air mattress overlay helps to reduce shear forces by allowing the body to move more freely without creating friction against the skin.
3. Promoting Proper Body Alignment
Maintaining proper body alignment is another crucial factor in preventing bedsores. When a patient’s body is not aligned correctly, pressure is unevenly distributed, leading to increased stress on certain areas of the skin and underlying tissue. For instance, improper alignment of the head, neck, and spine can lead to additional pressure on the shoulders and sacral region.
Positioning pads help to keep the body in a neutral, comfortable position by supporting key areas such as the head, neck, and joints. For instance, head cushions and neck rolls ensure proper head alignment while reducing pressure on the neck and shoulders. Knee pillows or foam wedges help keep the legs in alignment, reducing pressure on the hips and lower back. By supporting the body in its optimal position, positioning pads reduce the risk of pressure ulcers and help promote skin health.
4. Enhancing Comfort for Long-Term Immobility
For patients who are immobile for extended periods—such as those recovering from surgery, patients with spinal cord injuries, or those in critical care—prolonged pressure on certain areas can lead to skin breakdown. In these cases, positioning pads are crucial for enhancing comfort and preventing the formation of bedsores.
Positioning pads ease the pain of prolonged lying in one position by offering support and cushioning. For example, a foam mattress overlay or a gel pad provides comfort and pressure relief, helping to redistribute weight and prevent prolonged pressure on vulnerable areas. These pads not only reduce the risk of bedsores but also improve the patient’s overall comfort, which can enhance the healing process and prevent complications associated with immobility.
5. Facilitating Repositioning and Mobilization
Regular repositioning is key to preventing bedsores, but repositioning patients manually can be challenging, especially for those who are heavy, immobile, or in pain. Positioning pads can make repositioning easier and safer for both the patient and the caregiver.
For example, turning pads or slide sheets can assist in shifting the patient’s position with minimal friction, reducing the risk of shear and skin damage during the process. These pads help move the patient smoothly, avoiding unnecessary stretching or dragging of the skin, which can lead to injuries and ulcers. Additionally, positioning pads make it easier to maintain proper positioning during the repositioning process, further reducing the risk of pressure injuries.
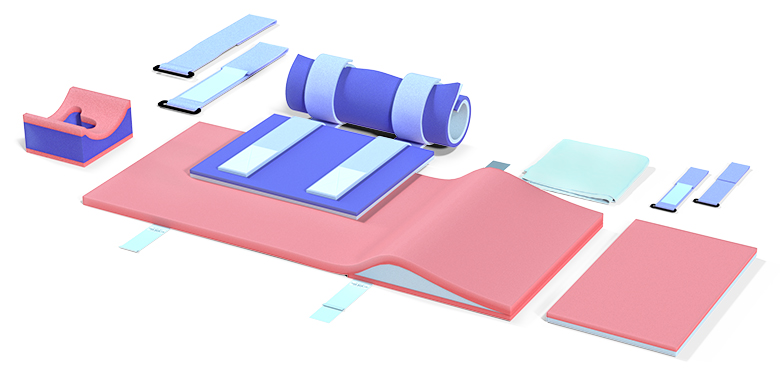
The Efficiency of Different Types of Positioning Pads
Several types of positioning pads are used in clinical practice to reduce bedsores and improve skin integrity. Every kind of pad is made to meet particular requirements and offer particular advantages:
- Foam Pads: Foam pads are often used in hospital beds, wheelchairs, and other seating arrangements. They provide excellent cushioning and pressure redistribution, making them ideal for patients who spend a lot of time in one position. Foam pads are lightweight, easy to use, and cost-effective.
- Gel pads are well-known for their exceptional pressure-relieving capabilities and capacity to mold to the contours of the body. They are often used for areas such as the heels, sacrum, and elbows, where pressure ulcers are most likely to occur. Gel pads are also durable and can be repositioned easily without losing their effectiveness.
- Air Pads and Mattresses: Air-filled cushions and mattresses provide continuous pressure relief by inflating and deflating in cycles. These devices are particularly effective for high-risk patients, as they help redistribute pressure and prevent the development of pressure ulcers. Mattresses with minimal air loss are commonly used in critical care units (ICUs) and long-term care facilities.
- Sheepskin Pads: Sheepskin is a natural material that provides both cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for patients with sensitive skin. Sheepskin pads are often used in conjunction with other forms of pressure relief to provide added comfort and skin protection.
- Air-Fluidized Beds: These beds use a combination of air and fluid-like materials to create a floating effect, which reduces pressure and promotes skin integrity. Air-fluidized beds are often used for patients who are at high risk of developing bedsores or those with existing ulcers that need specialized care.
Conclusion
Positioning pads are crucial in preventing bedsores and maintaining skin integrity by redistributing pressure, reducing friction, and supporting proper alignment. They protect sensitive skin, improve comfort, and make repositioning easier in healthcare environments like hospitals, assisted living facilities, and home care. When used with regular repositioning and other preventive measures, these pads significantly reduce bedsores and improve patient outcomes.